The 55th Paris-Le Bourget International Air and Space Exhibition grandly opened. With the exhibition theme of "All Value In Cooperation", AVIC brought a heavyweight showcase of 30 key aviation products across 8 major categories, including the new-generation stealth fighter J-20, J-35A stealth fighter and other "20" family series equipment, "Wing Loong" drone series, and AG600 - the world's largest civil amphibious aircraft by takeoff weight. Notably, the J-10CE, also participated in the exhibition.
These major national technological marvels collectively presented a hardcore feast of aviation technology from Eastern civilization to the global aviation community, fully demonstrating AVIC's innovative strength, systematic development achievements, and open cooperative attitude.

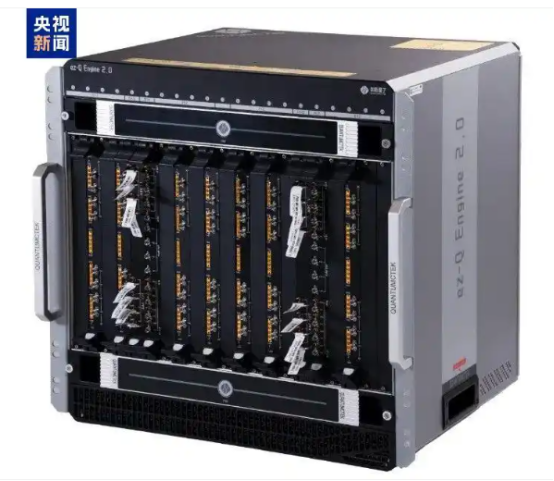
China's first superconducting quantum computing measurement and control system designed for the thousand-qubit scale, ez-Q Engine 2.0, has been officially delivered to institutions including the University of Science and Technology of China. As the core equipment for the "Zu Chongzhi-3" quantum computer, the system will provide measurement and control services for multiple institutions, supporting a cumulative capacity of over 5,000 qubits.

China successfully launched the electromagnetic monitoring satellite "Zhang Heng-1" 02 from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center using a Long March 2D carrier rocket. The rocket sent the satellite into its scheduled orbit, marking a complete success of the launch mission. This represents another major achievement in China's construction of detection capabilities in the field of geophysical field space observation, further enhancing China's "sky-air-ground" three-dimensional monitoring capacity for major natural disasters.

Yttrium-90 glass microspheres irradiated by Qinshan Nuclear Power's "Hefu-1" reactor have successfully been removed from the core and passed quality inspections, marking China's breakthrough in producing Yttrium-90 through commercial nuclear reactors and enabling mass production.
The Yttrium-90 glass microspheres are primarily derived from Yttrium-89, which becomes radioactive Yttrium-90 after absorbing neutrons in a nuclear reactor. As a beta radiation-emitting radiopharmaceutical, these microspheres are delivered via vascular interventional procedures to hepatic arteries, providing precise minimally invasive treatment for liver tumor lesions. This innovation leverages commercial reactor technology to address clinical needs, with the Hefu-1 reactor's stable neutron flux and large active core area ensuring scalable, cost-effective production.
The Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Huashan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University and relevant enterprises, has successfully conducted China's first prospective clinical trial of an invasive brain-computer interface (BCI).
The subject is a male who suffered limb amputation due to a high-voltage electrical accident. Since the BCI device was implanted in March 2025, the system has operated stably. With only 2 to 3 weeks of training, he has achieved functions such as playing chess and racing games, reaching a level comparable to ordinary people controlling a computer touchpad. In the future, this system is expected to improve the quality of life for patients with spinal cord injuries, amputations, and other conditions through motor function substitution technology.
